Population is the number of people that live in an area at a particular time.
It is clear how population in the 1800’s is not the same as today, and this
change in population has led to a change in the social characteristics of many
individuals within the population. The amount of population is not the only
thing that has changed, but also the way they are distributed. Population used
to be on separate small groups apart from each other. Population movement,
which will be furthered explained, has caused effects such as urbanization,
which is how population has been moving towards big cities and concentrating on
big cities. Many theories have been created to explain these changes in the
population and population movements worldwide.
The field of science that studies population is called demography.
Demographers measure the growth of a population by finding its birthrate.
The term fertility, when used by sociologists around the world, refers
to the actual number of births occurring to women of childbearing age.
Fecundity is different than fertility, fecundity refers to the biological
capability to bear children. Population is also affected by mortality,
which is the number of deaths within a society. Demographers call the amount of
deaths that occur in a society, death rate. When the death is of a kid
under the age of one, then it is included in the infant mortality rates,
which includes the record of all the deaths of children under 1 year old. The
average number of years that a person born in a particular year can expects to
live is called life expectancy. The third factor that demographers take
into account is migration, the number of individuals that are entering
the society and come from somewhere else. Demographers can calculate the migration
rate by finding the annual difference between migration and emigration. In
reality, the long-term effect of such a growth rate on population size is
related to a population’s doubling time.
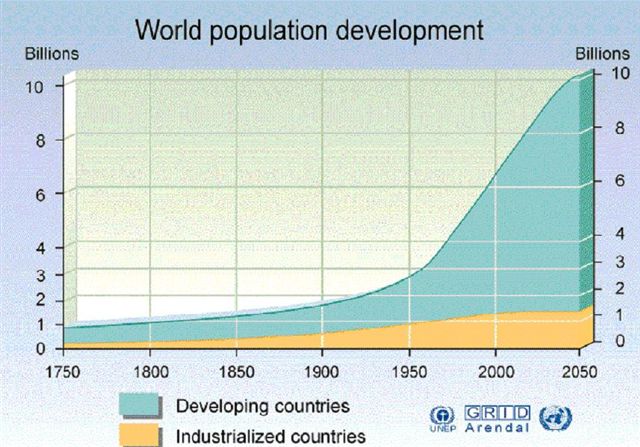
Population growth on the last decades.
Like mentioned
before, there are many theories that try to explain these phenomenon, some of
the following are part of the most respected by demographers around the world. The
demographic transition theory says that population patterns are tied to
a society’s level of technological development. If we were to follow the
demographic transition theory, there would be a point in which the stage three
population, or society, will reach a point in which its birth rates and death
rates are the same, so population won’t be neither increasing nor decreasing,
this phenomenon is called zero population growth. Viewing that
population might become a major 21rst century problem, many countries have
begun to promote family planning, which give many options to families to
be able to “plan” their children and not have families with many children,
instead have small families that will reduce the population.
Urbanization, urbanization is a
movement involves the concentration of the population in cities. To completely
understand the definition of urbanization it would be most proper to understand
some key terms of the definition, for example, “a city is a permanent
concentration of a relatively large number of people who are engaged mainly in
non-farming activities”. Over urbanization, “a situation in which more
people live in a city than can be supported in term s of jobs and facilities”,
has lately become a great problem in countries that are not yet that developed.
The concentric zone model which helps to describe urban structure was
created in 1925 by Ernest W. Burgess. The sector model argues that
growth occurs in wedge-shaped sectors, outward from the center of the city, the
multiple nuclei model, on the other hand, argues that a city does not
develop around one central core but around several centers of activity.
Unplanned cities, such as Tegucigalpa, follow a urban sprawl pattern,
which is characterized by poorly planned development on the edge of cities and
towns. Louis Wirth put forward an urban anomie theory. Compositional theory views the ways in
which the composition of a city’s population influences life in the city.
Population trends
have simply gone beyond what anyone would have ever imagined, growing from 1
billion 200 years ago, to over 7 billion today, just amazing, and, where is
this population at? 2004 was the official date when exactly 50% of the
population lived in rural areas and the other 50% in cities, that number must
be much more higher on the city side by now, now that’s what any sociologist
would call urbanization.
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario